Using Aggregate Functions
Learning Objectives
Basic Aggregate Functions
How to calculate totals, averages, etc. over multiple rows.
You frequently need to get a single piece of information that is derived from multiple rows in a table. For example, when you need to know the total of all invoices for August 2018:
SELECT sum(total)
FROM invoices
WHERE invoice_date BETWEEN
'2018-08-01' AND '2018-08-31';
The aggregate functions are:
- sum : Calculate the total of the values in a column
- avg : Calculate the average (mean) of the values in a column
- min : Determine the mimimum value of a column
- max : Determine the maximum value of a column
- count : Count the number of values (non-null) in a column
All the above are in the SQL standard, most implementations provide others. SUM and AVG can only apply to numeric data, the others can apply to any datatype.
Further examples:
“What is the average length of stay at our hotel?” :
SELECT avg(checkout_date - checkin_date)
FROM reservations;
“What are the lowest and highest room rates we charge?” :
SELECT min(rate) AS lowest,
max(rate) AS highest
FROM rooms;
You can use the count(x) function to count non-null values:
SELECT count(id) AS id_ct, count(postcode) AS post_ct
FROM customers;
id_ct | post_ct
-------+---------
133 | 126
(1 row)
Notice that these two results show different values - there are NULL values for postcode but id is mandatory for all rows.
If you just want to count the number of rows, use count(*). This is often used to find how many rows match a WHERE clause:
SELECT count(*) FROM customers WHERE country = 'Belgium';
Hotel Exercise 1
- Get the numbers of rows in each of the tables: rooms, room_types, customers and reservations.
- How many reservations do we have for next month?
- How many invoices are still unpaid from over a month ago and what is the total owed?
- What is the maximum gap in days between a customer booking a room and the checkin date for that booking?
Grouping Rows for Aggregation
You can calculate aggregates over subsets of rows using the GROUP BY clause:
SELECT count(*) FROM rooms
GROUP BY room_type;
count
-------
14
14
8
10
2
(5 rows)
What do you notice?
The query calculated the counts correctly but we have no idea which room type each value represents. To solve this we are allowed to include the GROUP BY expressions in the list of selected values, as below:
SELECT room_type, count(*) FROM rooms
GROUP BY room_type;
room_type | count
--------------+-------
PREMIUM | 14
PREMIER | 14
PREMIER PLUS | 8
PREMIUM PLUS | 10
FAMILY | 2
(5 rows)
Notice the room_type used for GROUP BY is also included in the SELECT list of values.
We can group by multiple expressions, for example:
SELECT trunc(room_no/100) AS floor,
to_char(checkin_date, 'YYYY-MM') AS month,
count(*), sum(no_guests), avg(no_guests)
FROM reservations
GROUP BY floor, month;
Notice that the GROUP BY is using the column aliases floor and month that have been defined in the select list. This works in many, but not all, SQL implementations. (In those that don’t allow aliases you must use the full expression, for example: trunc(room_no/100) instead of floor)
You can use a WHERE clause to restrict the rows that are included in the aggregate function. For example, if we need the above query for only the 2nd and 3rd floors:
SELECT trunc(room_no/100) AS floor,
to_char(checkin_date, 'YYYY-MM') AS month,
count(*), sum(no_guests), avg(no_guests)
FROM reservations
WHERE room_no BETWEEN 200 AND 399
GROUP BY floor, month;
Note that it is NOT usually possible to use column aliases in the where condition.
A WHERE clause is applied before any aggregation, if you need to restrict results using an aggregate function you can’t do that using the WHERE clause.
In the above, to return only results with the number of reservations greater than, say, 4 we use the HAVING clause:
SELECT trunc(room_no/100) AS floor,
to_char(checkin_date, 'YYYY-MM') AS month,
count(*), sum(no_guests), avg(no_guests)
FROM reservations
GROUP BY floor, month
HAVING count(*) > 4; --<< Note the HAVING keyword
The order of clauses in the SELECT statement is:
SELECT ...
FROM ...
[WHERE ...]
[GROUP BY ...
[HAVING ...] ]
[ORDER BY ...]
The square brackets indicate optional clauses. Note that HAVING is only relevant when you have a GROUP BY and must follow it in the SELECT statement.
It can be confusing at first knowing whether to use a WHERE clause or a HAVING clause with GROUP BY.
Use the
WHEREclause when values you want to test are available without having to use any aggregate functions (e.g. plain column values).Use
HAVINGwhen the values you want to test are the results of aggregate functions (e.g.count(*),sum(amount),min(x), etc…).
Hotel Exercise 2
- What is the grand total of all invoices for each month?
- How many guests could be accommodated at one time on each floor?
- Which rooms have been occupied for less than 10 nights and for how many nights have they been occupied?
Inserting, Updating and Deleting Rows
Learning Objectives
Inserting data
To add new data to a table use the INSERT command that has the following format:
INSERT INTO table_name (column_name, ...)
VALUES (value, ...)
For example:
INSERT INTO customers (name, email, address, city, postcode, country)
VALUES ('John Smith','j.smith@johnsmith.org',
'11 New Road','Liverpool','L10 2AB','UK');
Note:
- You do not need to supply the value for the automatically generated
idcolumn, it is populated from a sequence generator object. - The order of values in the
VALUES (...)clause must correspond to the columns in the column name list. The first value is stored in the first named column, the second value in the second named column and so forth.
Hotel 3
- Insert yourself in the
customerstable. Query the table to check your new data. - Insert a new room type of PENTHOUSE with a default rate of 185.00.
Updating Existing Data
When you need to change values in a table, use the UPDATE command. The general construction to update a row is:
UPDATE table
SET column1 = value1,
column2 = value2
WHERE condition;
Note that UPDATE usually requires a WHERE clause to specify the row or rows to be updated. As with SELECT, if you don’t specify a condition to restrict the rows, the command applies to all the rows in the table.
For example, to update the name and country of the customer with ID 3:
UPDATE customers
SET name='Bob Marley',
country='Jamaica'
WHERE id=3;
Hotel 4
- Update the postcode of the customer named
Alice EvanstoM21 8UP - Update room 107 to allow up to 3 guests
- For the customer named
Nadia Sethuraman, update her address to2 Blue Street, her city toGlasgowand her postcode toG12 1ABin one query - Update all the future bookings of customer with ID 96 to 3 nights (starting on the same check-in date) in one query
Deleting a row
The syntax to delete a row is:
DELETE FROM table WHERE condition;
For example, to delete the booking with ID 4:
DELETE FROM reservations WHERE id=4;
NOTE
WHERE clause with DELETE or UPDATE the command will be applied to all the rows in the table which is rarely what you want.Hotel 5
- Delete the bookings of customer ID
108that do not have a room number assigned - Delete all the bookings of customer Juri Yoshido (customer id 96)
- Delete the customer details for Juri Yoshido
Joining Tables
Learning Objectives
Introduction
So far we’ve only looked at one table in any query. Many problems require data from several tables - how do we do that?
For example, if I want to phone or email customers who have not yet paid their invoices, which tables do I need to look at?
Use joins to combine data from more than one table. Joins use column values to match rows in one table to rows in another.
The join columns are usually referred to as foreign keys and primary keys.
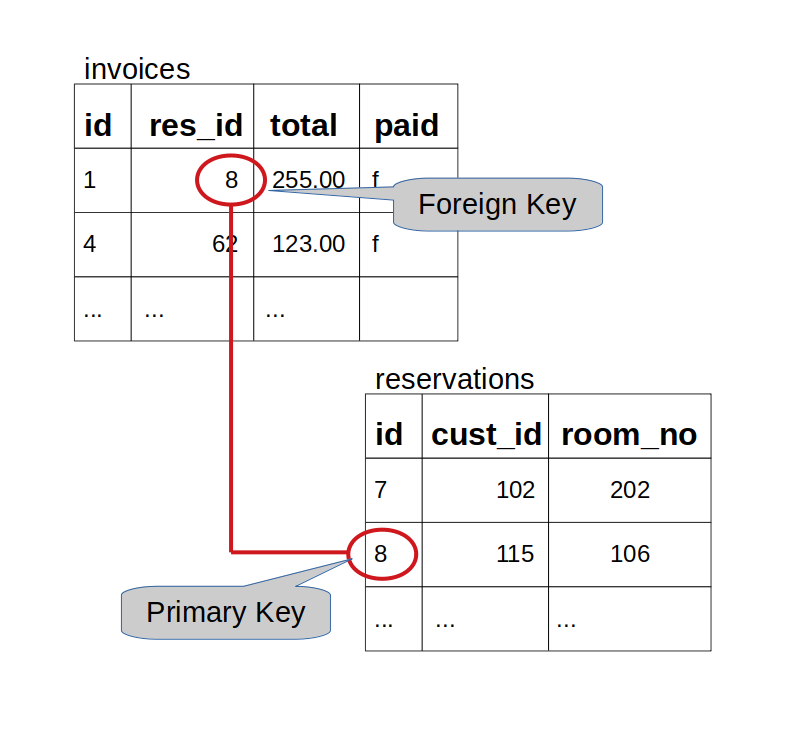
Foreign and Primary Keys
Each table should have a Primary Key. This is one or more columns whose values, which cannot be NULL, are combined to provide a unique identifying value for each row. Natural primary keys are often difficult to find so many tables use an arbitrary integer whose value is automatically generated when the row is created. When joining tables we need to match a single row to one or more other rows, usually in another table - for example, matching a customer to her/his reservations. The single row (customer) is usually identified by its primary key value.
Foreign Keys are the columns in a table that reference corresponding columns in another table (although self-referencing foreign keys can reference the same table). For example, the res_id column in the invoices table references the id column in the reservations table (see diagram above).
The referenced column is almost always the primary key of the referenced table because a foreign key must always reference exactly one row in the referenced table (primary keys guarantee that).
Using JOIN in SQL
To join reservations and invoices in SQL:
SELECT r.cust_id, r.room_no, i.invoice_date, i.total
FROM reservations r JOIN
invoices i ON (r.id = i.res_id);
Notice:
- The new keyword JOIN with ON (predicate)
- Table aliases (
randi) used to qualify columns
The new syntax follows the following pattern:
SELECT ...
FROM ... [JOIN ... ON (...)]...
[WHERE ...]
[GROUP BY ... [HAVING ...] ]
[ORDER BY ...]
Use the JOIN to define the combined row source then you can use WHERE, DISTINCT, GROUP BY, ORDER BY, etc… as with single-table queries. For example:
SELECT r.cust_id, r.room_no, i.invoice_date, i.total
FROM reservations r JOIN
invoices i ON (i.res_id = r.id)
WHERE r.checkin_date > '2018-07-01'
AND i.total < 500
ORDER BY i.invoice_date DESC, r.cust_id;
There is no theoretical limit to the number of tables that can be joined in a query, although practical considerations like
complexity and performance must be considered. It is quite common, though, to find up to seven or eight tables joined in a query.
Multi-table joins just extend the syntax to add more tables, as below:
SELECT c.name, c.phone, c.email, i.invoice_date, i.total
FROM customers c JOIN
reservations r ON (r.cust_id = c.id) JOIN
invoices i ON (r.id = i.res_id)
WHERE i.invoice_date < current_date - interval '1 month'
AND i.paid = FALSE
ORDER BY i.invoice_date DESC, c.id;
Note
You have just learned about what is called the INNER JOIN, which is the most common kind of join. Indeed, you can use the keyword INNER in the JOIN syntax, as follows:
SELECT c.name, c.phone, c.email, i.invoice_date, i.total
FROM customers c INNER JOIN
reservations r ON (r.cust_id = c.id) INNER JOIN
invoices i ON (r.id = i.res_id)
WHERE i.invoice_date < current_date - interval '1 month'
AND i.paid = FALSE
ORDER BY i.invoice_date DESC, c.id;
The INNER keyword is not required (it’s the default) but some organisations might require it for the sake of coding standards.
There are other kinds of JOIN, specifically the OUTER JOIN and the CROSS JOIN but these are less frequently used in applications.
If you want to find out about these kinds of JOIN refer to the PostgreSQL documentation.
Exercise 5
- Try and understand each of the queries above in your
psqlprompt - Which customers occupied room 111 and what are their details?
- List the customer name, room details (room number, type and rate), nights stay and departure dates for all UK customers.
- List name, phone and email along with all reservations and invoices for customer Mary Saveley.
The Vexing Question of NULL
A column can be assigned a NULL value to indicate it has no value. This can happen when the data for this column is unknown at the time the row is created, for example, employee leaving date, order shipment date, etc… It can also be used when the data is optional.
Be careful with expressions - any expression that includes a NULL value results in NULL as the expression value.
Because NULL is ’no value’ it cannot be compared to anything else. For example, you will never get any results from:
SELECT * FROM customers WHERE postcode = NULL;
nor will you get any from:
SELECT * FROM customers WHERE postcode != NULL;
Instead you must use:
... WHERE postcode IS NULL
or
... WHERE postcode IS NOT NULL
This behaviour has some impacts on operations like JOIN, where NULL values won’t match. You could work around this, but see the warning below, by using:
... ON (a.col = b.col OR
a.col IS NULL AND b.col IS NULL)
WARNING:
However, be aware that this is not a sensible situation - join columns containing NULL should be expected to not match or should be disallowed (see Primary Keys above)
You can explicitly provide NULL as a value in INSERT and UPDATE statements, for example:
INSERT INTO rooms (room_no, rate, room_type, no_guests)
VALUES (213, 95.00, NULL, 2);
UPDATE rooms SET room_type = NULL, no_guests = NULL
WHERE room_no = 204;
In INSERT statements if you omit a column from the column list (following the table name) then that column will be given either:
- an autogenerated value (if it has datatype SERIAL)
- a default value if one has been specified in the CREATE TABLE command
- NULL if neither of the above apply
Functions to Handle NULL
There are some functions that can operate on NULL values, especially the coalesce(x, y) function. This function looks at the first argument x and if it is NULL returns the value of the second argument y otherwise it returns the value of x. For example:
SELECT room_no, rate, coalesce(room_type, 'None') type
FROM rooms
WHERE no_guests IS NULL;
Notes:
- The coalesce function can take more than two arguments and returns the first of these (from left to right) that is not null.
- This feature is provided by most SQL vendors but goes by different names, e.g. ifnull(x, y) in MySQL, nvl(x, y) in Oracle, etc…
Exercise 6
- Which customers have not yet provided a phone number?
- Update room 304 such that it does not have a room_type.
- List customers (name and city) qand their reservations replacing the room number with ‘Not Assigned’ if it is NULL.
Creating a table
Learning Objectives
Use the CREATE TABLE command, which in the simplest case has the general form:
CREATE TABLE <tablename> <column definition>, <column definition>, ...);
To create an inventory table for our hotel we might need:
CREATE TABLE inventory (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
description VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL,
cost NUMERIC(6,2)
);
Note: you may never need to do this. Database design is a task that requires specialist skills and considerable experience.
Naming Tables and Columns
In the CREATE TABLE command you must give the name of the table (e.g. inventory) and the names of each of the columns (in the parenthesised column definitions) (e.g. id, description, cost).
Names of tables and columns (and any other objects in the database) must start with a letter, can contain letters, digits and the underscore symbol (_) up to 64 bytes (in PostgreSQL). Names are not case-sensitive so that NAME, name and NaMe are all the same.
Data Types of Columns
In the above example:
| Column | Data Type | Other |
|---|---|---|
id | SERIAL | PRIMARY KEY |
description | VARCHAR(30) | NOT NULL |
cost | NUMERIC(6,2) |
The id column uses SERIAL as its data type, making it an autoincrementing integer that increments by 1, starting from 1, for each time a new row is inserted into the table. For this to work, the id column must be omitted from the INSERT command. id is also designated as the PRIMARY KEY of the table (note that SERIAL doesn’t make the column the primary key). PRIMARY KEY also implies that the column cannot be set to NULL.
The description column is a variable length character value (VARCHAR) that can hold up to a maximum of 30 characters. The NOT NULL constraint means the value cannot be left empty, each row must have a description.
The cost column is NUMERIC(6,2), a number that can accurately store up to 6 digits, two of which are the fractional part. For example, it can hold 1234.56, -23.45 or 0.01. Note that the NUMERIC data type stores and computes values using decimal values and does not lose accuracy in the same was as, say, floating point values. NUMERIC values take longer in calculations because they don’t use simple binary values - user either integer or floating point for speed with compute-heavy numbers.
NEVER use floating point for financial values.
Other Common Data Types
There are several more standard data types (plus a few non-standard ones), including:
| Type | Notes |
|---|---|
| INTEGER | binary integer with 32 bits (range approx -2 x 109 – +2 x 109) |
| DATE | dates with no time component |
| TIMESTAMP | date and time (accurate to milliseconds) |
| BOOLEAN | TRUE, FALSE or NULL |
| TEXT | variable length text with no length limit (up to max allowed for the RDBMS - about 1Gb in PostgreSQL) |
You can read more about data types in the PostgreSQL documentation. Refer to https://www.postgresql.org/docs/12/datatype.html
for more information.
Changing a Table Definition
Using the ALTER TABLE command to add and remove columns:
ALTER TABLE inventory ADD COLUMN room_no INTEGER;
ALTER TABLE customers DROP COLUMN phone;
There are some constraints on adding and removing columns, for example, you cannot add a NOT NULL column to a table that already contains some rows.
Exercise 7
- Create a table for charge points. This must record the hotel shops, bars, cafes and restaurants that a customer can use during their stay.
- Include an auto-incrementing primary key
- Include the charge point name, a description and maximum customer credit value
- Insert charge points for ‘Shop’, ‘Pool Bar’, ‘Elysium Restaurant’ and ‘Room Service’ with credit limits of £1000 for each.
- Create a table for charge items that records amounts charged to rooms by customers using our shop, bars, restaurants, etc. This must include the room number of the room charged, the charge point used, the amount, the date and time of the charge and any customer comments.
Defining Primary and Foreign Keys
Learning Objectives
Defining Primary and Foreign Keys
Defining Primary Keys
Use the following templates to define a Primary Key.
For a single-column PK use:
CREATE TABLE <table name> (
...
<column name> <data type> PRIMARY KEY,
...
)
For example:
CREATE TABLE rooms (
room_no INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
...
);
To define a multi-column primary key you must define a constraint separate from the column definitions, as below:
CREATE TABLE <table name> (
...
<pk col 1> <data type>,
<pk col 2> <data type>,
... ,
PRIMARY KEY (<pk col 1>, <pk col 2>),
...
);
For example:
CREATE TABLE invoice_items (
inv_id INTEGER REFERENCES invoices(id),
item_no INTEGER,
... ,
PRIMARY KEY (inv_id, item_no),
...
);
There can be only one primary key in a table definition. The PRIMARY KEY definition implies NOT NULL so no column in a table’s PK can be set to NULL.
Note: a partial primary key can be a foreign key as well.
Defining Foreign Keys
To define foreign keys use either:
For a single-column foreign key:
<column name> <data type> REFERENCES <table name> (<column name>);
where the <column name> in the REFERENCES clause is the column name in the referenced table, not the one being defined at this point. For example, in the reservations table:
...
cust_id INTEGER NOT NULL REFERENCES customers (id),
...
For multi-column foreign keys we must again use a separate constraint definition, as shown:
CREATE TABLE customer_challenges (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
inv_id INTEGER,
item_no INTEGER,
...
FOREIGN KEY (inv_id, item_no) REFERENCES invoice_items (inv_id, item_no),
...
);
Exercise 8
- Try to delete the customer Mary Saveley. What happens and why?
- Insert a new room, number 313 as room type ‘SUPER PREMIER’.
- Define primary and foreign keys required by the charge_items table
- Insert some rows into the charge_items table. You can invent the details.
Integration with NodeJS
Learning Objectives
Introduction to node-postgres
“node-postgres is a collection of node.js modules for interfacing with your PostgreSQL database.” - https://node-postgres.com/
In the following, we will use node-postgres to…
- Connect to a database
- Send SQL queries to the database and get results
Loading data from a database with a GET endpoint
Let’s build a brand new NodeJS application with a single GET endpoint to load the list of customers that you already have in the customers table of the CYF_hotels database.
First, create a new NodeJS application that we will call CYF-hotels-api (enter server.js when asked for the entry point):
mkdir CYF-hotels-api
cd CYF-hotels-api
npm init
As before, we will use the Express library to build our API, and the node-postgres library to connect with our database:
npm install --save express
npm install --save pg
Create a server.js file, import express, initialise the server and start listening for requests:
const express = require("express");
const app = express();
app.listen(3000, function () {
console.log("Server is listening on port 3000. Ready to accept requests!");
});
Import pg library and create a new GET endpoint to load the list of customers:
const { Pool } = require("pg");
const db = new Pool({
user: "keith", // replace with you username
host: "localhost",
database: "CYF_hotels",
password: "",
port: 5432,
});
app.get("/customers", function (req, res) {
db.query("SELECT id, name, city, phone FROM customers")
.then((result) => {
res.json(result.rows);
})
.catch((error) => {
console.log(error);
});
});
In the code above:
- We first import the
Poolclass from the pg library, which is used to connect to a database - We create a new connection (
db) where we specify the credentials to connect to the CYF_hotel database - We then create a new
/customersendpoint where we use the methodquery()to send a SQL query to load all the customers from the tablecustomersand return the results withresult.rows. Thequerymethod returns a Promise: so we can access the returned rows using a.thenblock. You can write any valid SQL query that you learned in thequery()method!
Note: There is no semicolon to end the SQL statement.
Start your server with node server.js and try to reach the /customers endpoint to see the list of customers currently available in your CYF_hotels database. You can try to create/update/delete customers using psql to verify that your API always returns what is stored in your database.
Find and analyse a Job Description - Prep
🤙🏽 FeedbackLearning Objectives
Introduction
There is a dance that happens between the hiring manager, an HR department, recruiters and you. Your goal is to find a great job, and they want to find a great developer. The Job Description is part of this dance, but it is not always clear.
These exercises will help you understand job descriptions so that you don’t waste your time applying for the wrong opportunities and don’t miss what may be great opportunities.
Find a Job Description
🎯 Goal: Find a job posting that reasonably matches the kind of job you want. (30 minutes)
- Pick one of your favourite job search engines. Google, Indeed, LinkedIn, it-jobs.
- Search for available jobs that you are targeting. Possible search terms would be “entry-level”, “junior”, “front-end developer”, or “full stack developer”.
- Scan through each job description and find ONE that gives you a good initial feeling. There is a balance to be struck. Be realistic - there’s no point considering jobs you might want but require commercial experience you don’t yet have. But also realise that the job description is probably written by a combination of a hiring manager and an HR department who may describe a long list of desired skills that may never exist in a single human being! So don’t rule out jobs that don’t perfectly fit.
Note: some research has found that more women tend to believe that the listed “job requirements” are really required than men do. Don’t make the mistake of ignoring what might be your perfect job just because the job description doesn’t perfectly match your skills.
You will further analyse this job description in the next exercise.
Analyse Job Description
🎯 Goal: Consider how well the job matches your skills, how well the company interests you and whether or not there are any red flags. (45 minutes)
Re-read the job description, but this time, make notes on the following elements. Be ready to bring your notes to the session on Saturday because you will review them with a partner. If you want, you can copy and use this template to make your notes.
Core and extra requirements. Most job descriptions indicate whether requirements are core (mandatory, must have) or extra (desired, preferred, nice to have). Make a list of which requirements you meet and which you don’t.
Tip 1: make sure your CV is updated with any requirements that Job Descriptions are listing but that you may have forgotten to mention.
Tip 2: if there are required skills that you don’t currently have, and you are interested in developing them, consider adding these to your Development Plan.
Company values. Job descriptions will usually give information about the company and what matters to them. It is important that you feel there is a good match to your values. Do you care whether it is a large enterprise or a startup? Do you like their work-from-home/office policy? Reading between the lines, can you tell anything about their culture and whether it suits you? You can also check the company’s LinkedIn posts, website or references on Glassdoor to identify their culture.
Keywords. Are there phrases, terms or ideas that are repeated in the job description? This likely means that these are more important to the hiring manager. Take note of these because you should certainly include them in your cover letter if you apply. A good way of identifying these is using a word cloud.
Tip: make sure that you explicitly include these keywords in your Cover Letter. For example, if “collaboration in agile teams” is a repeated theme in the Job Description, your Cover Letter needs to include something about how good a fit this is for you.
Red flags. Certain phrases in job descriptions may provide warning signs for you. Can you spot any? Examples:
- “Go the extra mile”, “put in long hours”, or “high-paced environment”. Does this mean you won’t be able to have a reasonable work/life balance?
- “Must cope well with stress”. Does this mean that their projects are very stressful?
- “Must be a self-starter”. Does this mean there will be nobody to help you?
- The job is listed as “entry-level” but requires that you have years of experience. Does this mean they want to pay an “entry-level” salary for someone with much more experience?
- Unreasonably long list of requirements that includes the skills of five people. Does this mean the hiring manager has unrealistic expectations?
Questions. What questions occur to you as you re-read the job description? Do you want them to clarify any of the red flags? Do you want to understand why they are posting this job? Do you want to understand more about their pain points? Which questions would you ask before an interview and which during?
Should you apply? Having done the above assessment, how likely are you to apply for this job?
Good interview questions
🎯 Goal: Be prepared with some good messages and questions for your interview (15 minutes)
Read this Harvard Business Review article (or watch the video if you prefer) about good questions to ask during an interview.